Chapter
7--
Circulation of the Atmosphere
REMEMBER TO READ THE CHAPTERS IN THE TEXT BOOK
TEST 3 NOVEMBER 10TH, Chapter 6, 7 and 8.
CHAPTER 7 VIDEO -(204 views)
Important pages 182-193
BELOW VIDEO CHAPTER 7 AND CHAPTER 8. (285 views)
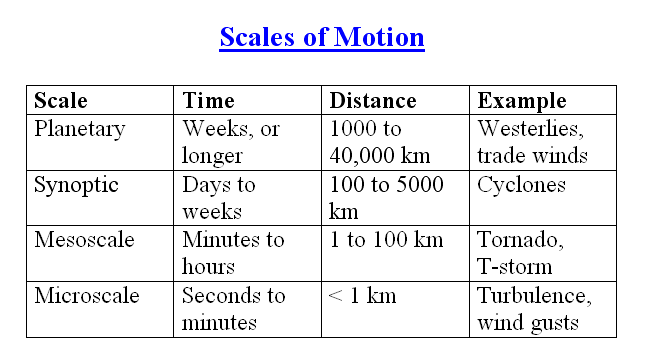
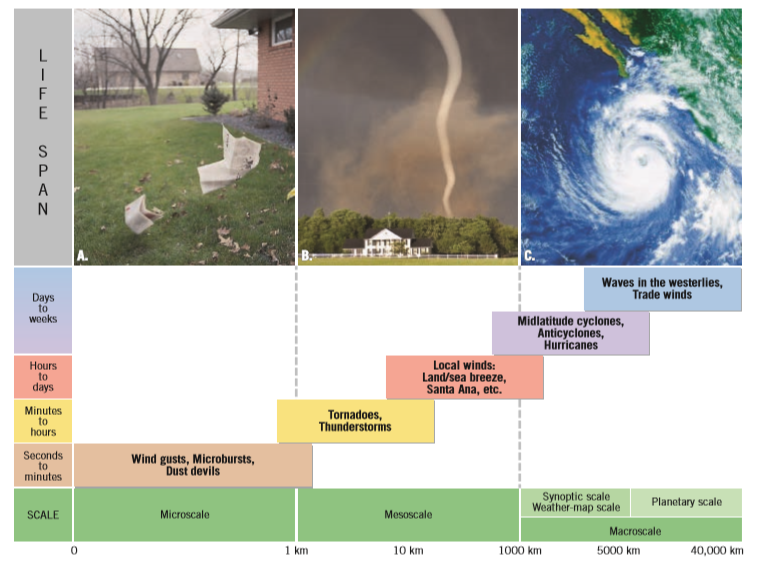
The largest planetary-scale wind patterns, called macroscale
winds, include the westerlies and trade winds. A somewhat smaller macroscale
circulation is called synoptic scale, or weather-map scale. Mesoscale winds,
such as thunderstorms, tornadoes, and land and sea breezes, influence smaller
areas and often exhibit intensive vertical flow. The smallest scale of air
motion is the microscale. Examples of these very local, often chaotic, winds
include gusts and dust devils.
Scales of Atmospheric Motion
categorized according to average size and lifespan
macroscale (planetary scale) - longwaves in the westerlies
synoptic scale (weather map scale) - cyclones, anticyclones
mesoscale - thunderstorms, tornadoes, land and sea breeze
microscale - turbulence, wind gust
----->>>>>>READ PAGES 176-180 <------
 |
 |
 |
 |
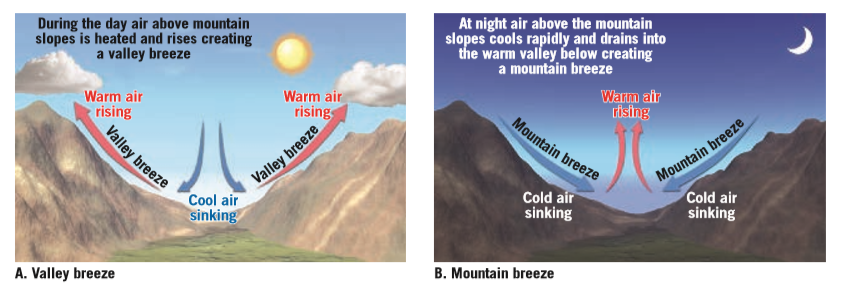
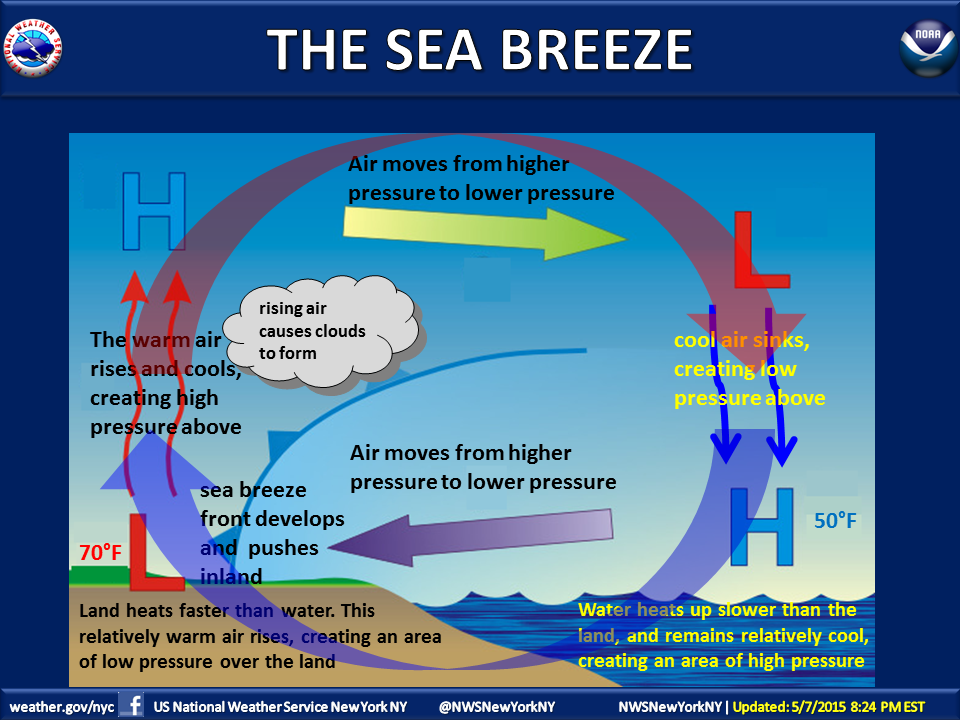
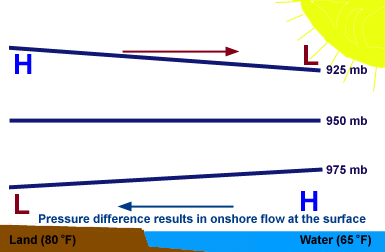
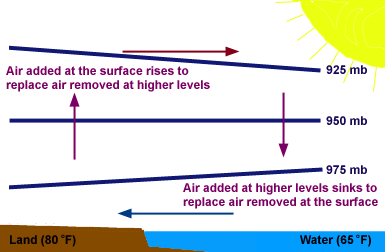
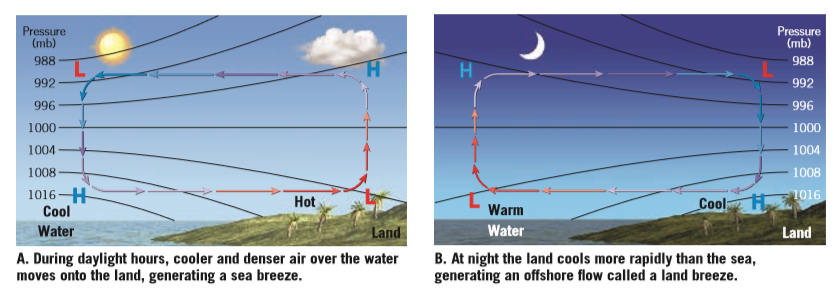
All winds have the same cause: pressure differences that arise because of temperature differences that are caused by unequal heating of Earth's surface. In addition to land and sea breezes brought about by the daily temperature contrast between land and water, other mesoscale winds include mountain and valley breezes, chinook (foehn) winds, katabatic (fall) winds, and country breezes.
 |
 |
 |
 |
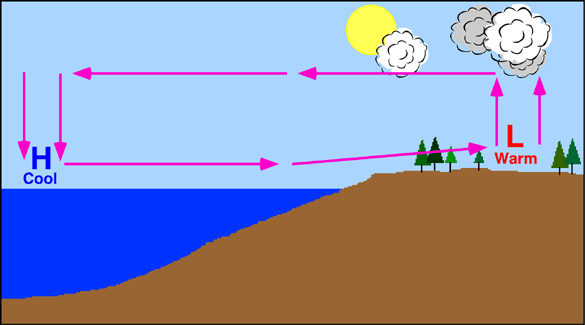 |
Mountain and valley breezes develop as air along mountain slopes is heated more intensely than air at the same elevation over the valley floor. Chinooks are warm, dry winds that sometimes move down the east slopes of the Rockies. In the Alps, winds similar to chinooks are called foehns. Katabatic (fall) winds originate when cold air, situated over a highland area such as the ice sheets of Greenland or Antarctica, is set in motion under the influence of gravity. Country breezes are associated with large urban areas where the circulation pattern is characterized by a light wind blowing into the city from the surrounding countryside.
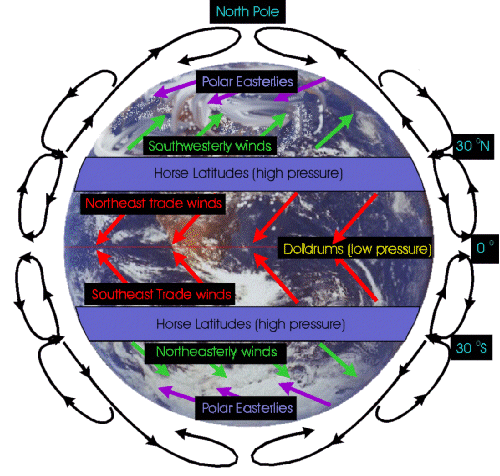
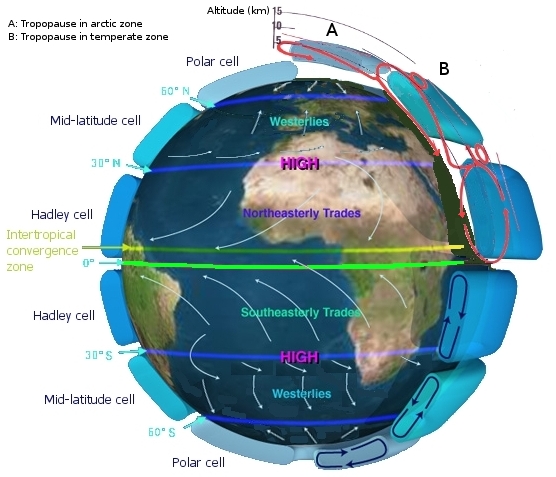
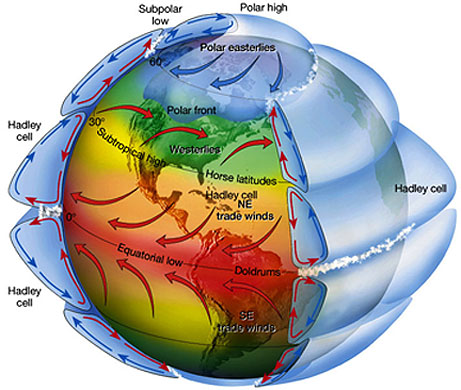
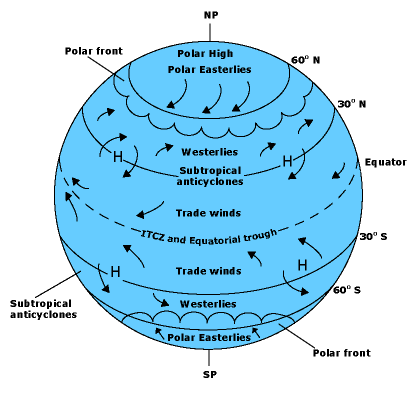
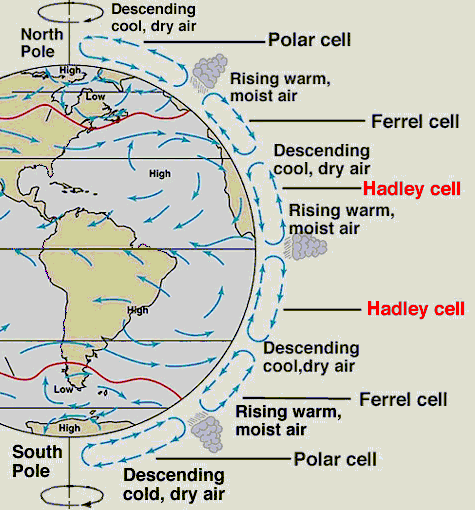
A simplified view of a model of global circulation is a three-celled
circulation model for each hemisphere. Because the circulation patterns between
the equator and roughly 30° latitude north and south closely resemble
an earlier single-cell model used by George Hadley in 1735, the name Hadley
cell is generally applied. According to the three-cell circulation model,
in each hemisphere, atmospheric circulation cells are located between the
equator and 30° latitude, 30 and 60° latitude, and 60° latitude
and the pole. The areas of general subsidence in the zone between 20 and 35°
are called the horse latitudes. In each hemisphere, the equatorward flow from
the horse latitudes forms the reliable trade winds. Convergence of the trade
winds from both hemispheres near the equator produces a region of light winds
called the doldrums. The circulation between 30 and 60° latitude (north
and south) results in the prevailing westerlies. Air that moves equatorward
from the poles produces the polar easterlies of both hemispheres. The area
where the cold polar easterlies clash with the warm westerly flow of the midlatitudes
is referred to as the polar front, an important meteorological region.
VERY VERY IMPORTANT --- UNDERSTAND WHAT HAPPENS NEAR EACH LATITUDE LINE READ PAGE 182-193
Near 90 degrees North - Polar High
90 degreesNorth to 60 Degrees North - Polar Easterlies
Along or Near 60 Degrees North - Sub Polar Low or Polar Front
60 Degrees to 30 Degrees North - Westerlies
Along or Near 30 Degrees North - Subtropical High - Horse Latitues(over the Atlantic Ocean)
30 Degrees North to Equator - Northeast Trade Winds
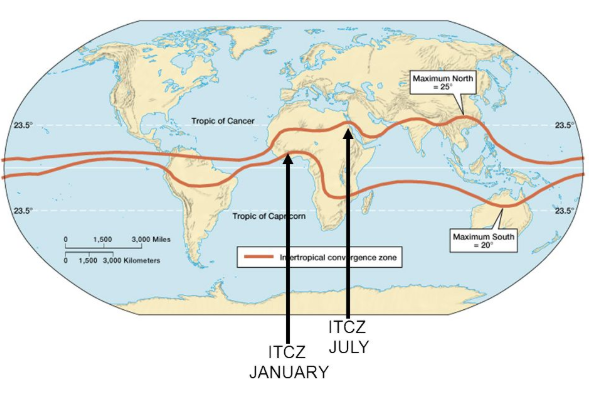
Along the Equator -
Equatorial Low, also referred to as the intertropical
convergence zone (ITCZ) because it is the region where the trade winds converge. Doldrums
30 Degrees South to the Equator - Southeast Trade Winds
Read pages 182-193 for images below.
 |
 |
 |
 |
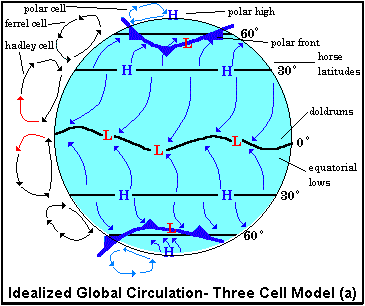
If Earth's surface were uniform, two latitudinally oriented
belts of high and two of low pressure would exist. Beginning at the equator,
the four belts would be the (1) equatorial low, also referred to as the intertropical
convergence zone (ITCZ) because it is the region where the trade winds converge,
(2) subtropical high, at about 20 to 35° on either side of the equator,
(3) subpolar low(Polar Front), situated at about 50 to 60° latitude, and (4) polar
high, near Earth's poles near 90 degrees..
 |
 |
In reality, the only true zonal pattern of pressure exists along the subpolar low in the Southern Hemisphere. At other latitudes, particularly in the Northern Hemisphere, where there is a higher proportion of land compared to ocean, the zonal pattern is replaced by semipermanent cells of high and low pressure. January pressure and wind patterns show a very strong high-pressure center, called the Siberian high, positioned over the frozen landscape of northern Asia. Also evident in January, but absent in July, are two intense semipermanent low-pressure centers, the Aleutian and Icelandic lows, situated over the North Pacific and North Atlantic, respectively. With the onset of summer the pressure pattern over the Northern Hemisphere changes dramatically and high temperatures over the continents generate lows that replace the winter highs. During the peak summer season, the subtropical high found in the North Atlantic (called the Azores high in winter) is positioned near the island of Bermuda and called the Bermuda high.
The greatest seasonal change in Earth's global circulation is the development of monsoons, wind systems that exhibit a pronounced seasonal reversal in direction. The best-known and most pronounced monsoonal circulation, the Asian monsoon found in southern and southeastern Asia, is a complex seasonal change that is strongly influenced by the amount of solar heating received by the vast Asian continent. The North American monsoon (also called the Arizona monsoon and Southwest monsoon), a relatively small seasonal wind shift, produces a dry spring followed by a comparatively rainy summer that impacts large areas of southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico.
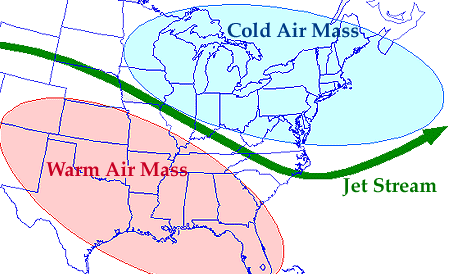
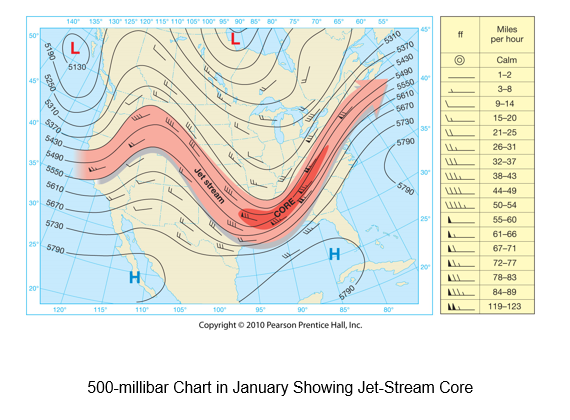
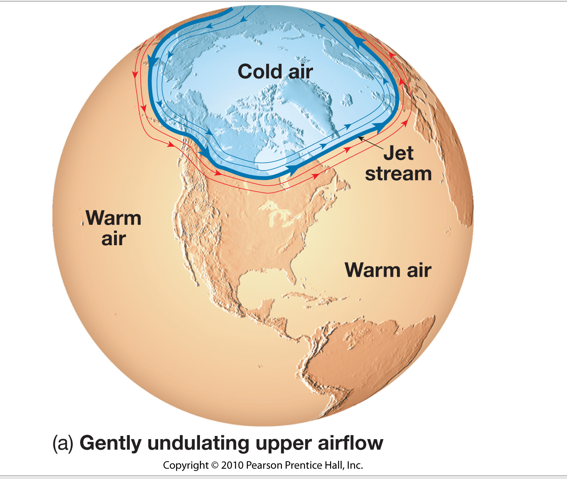
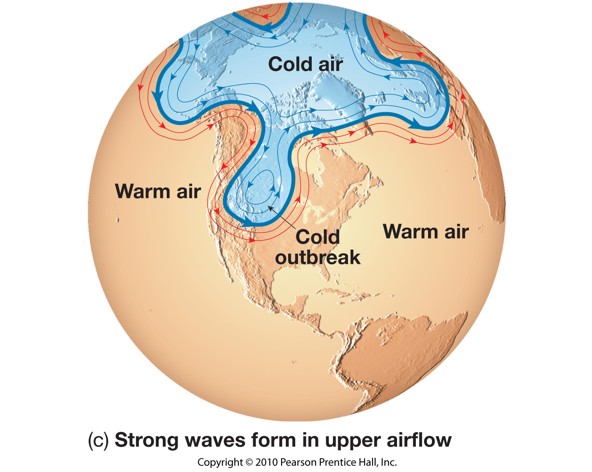
The temperature contrast between the poles and equator drives
the westerly winds (westerlies) located in the middle latitudes. Embedded
within the westerly flow aloft are narrow ribbons of high-speed winds, called
jet streams, that meander for thousands of kilometers. The key to the origin
of polar jet streams is found in great temperature contrasts at the surface.
In the region between 30 and 70°, the polar jet stream occurs in association
with the polar front.

 |
 |
 |
READ PAGES 190-195
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
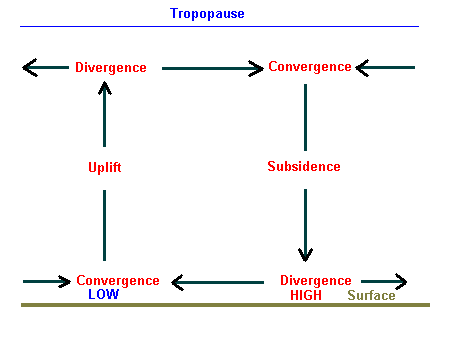 |
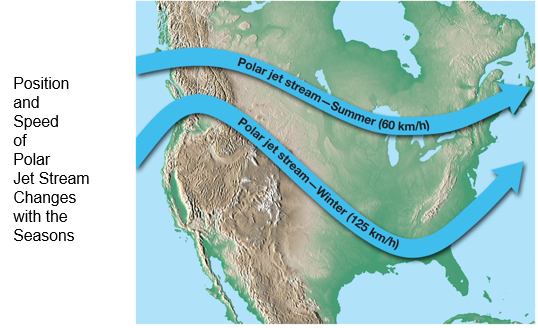
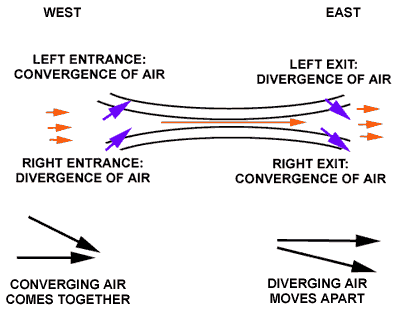
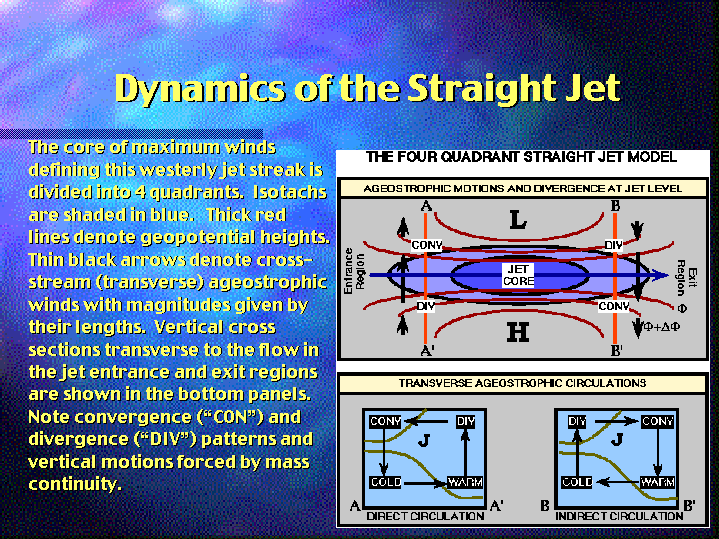
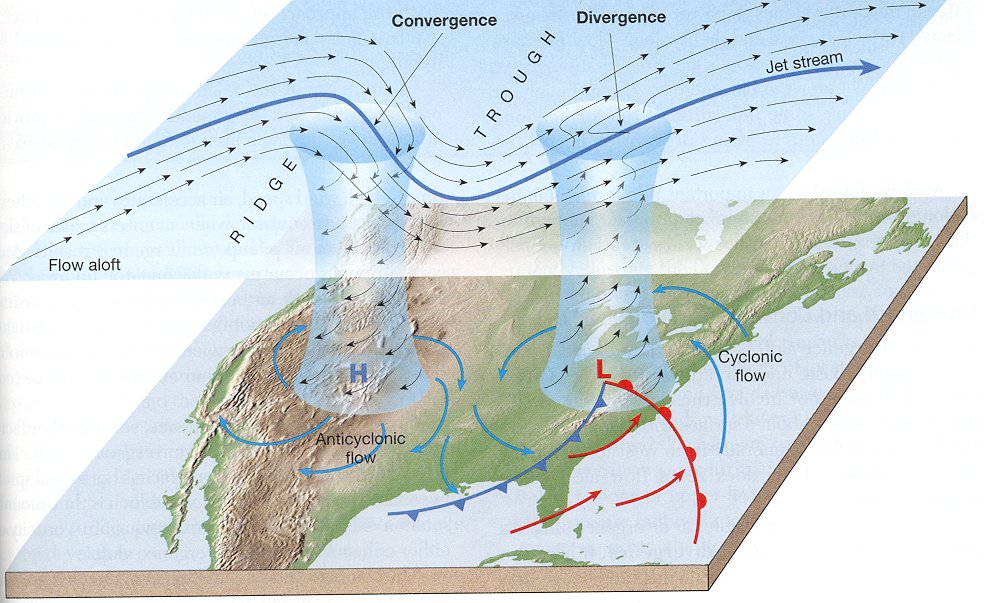
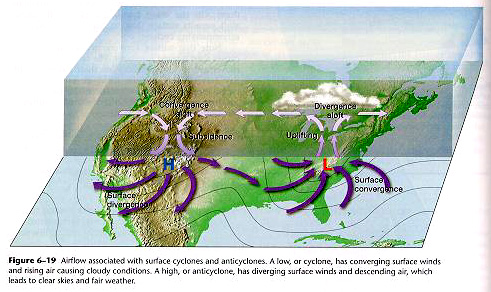
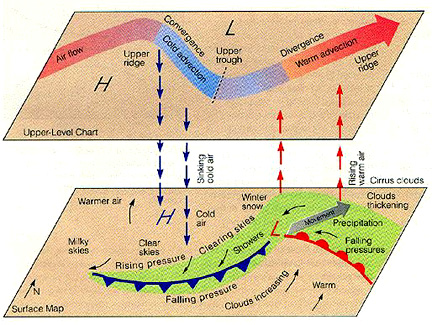
Studies of upper-level wind charts reveal that the westerlies follow wavy paths that have rather long wavelengths. The longest wave patterns are called Rossby waves. During periods when the flow aloft is relatively flat, little cyclonic activity is generated on the surface. Conversely, when the flow exhibits large-amplitude waves having short wavelengths, vigorous cyclonic storms are created. In addition to seasonal changes in the strength of its flow, the position of the polar jet also shifts from summer to winter.
Because winds are the primary driving force of ocean currents, a relationship exists between the oceanic circulation and the general atmospheric circulation. In general, in response to the circulation associated with the subtropical highs, ocean currents form clockwise spirals in the Northern Hemisphere and counterclockwise spirals in the Southern Hemisphere. In addition to influencing temperatures of adjacent land areas, cold ocean currents also transform some tropical deserts into relatively cool, damp places that are often shrouded in fog. Furthermore, ocean currents play a major role in maintaining Earth's heat balance. In addition to producing surface currents, winds may also cause vertical water movements, such as the upwelling of cold water from deeper layers to replace warmer surface-water.
El Niño refers to episodes of ocean warming caused by a warm countercurrent flowing southward along the coasts of Ecuador and Peru that replaces the cold Peruvian current. The events are part of the global circulation and related to a seesaw pattern of atmospheric pressure between the eastern and western Pacific called the Southern Oscillation. El Niño events influence weather at great distances from Peru and Ecuador. Two of the strongest El Niño events (1982–83 and 1997–98) were responsible for a variety of weather extremes in many parts of the world. When surface temperatures in the eastern Pacific are colder than average, a La Niña event is triggered. A typical La Niña winter blows colder than normal air over the Pacific Northwest and the northern Great Plains, while warming much of the rest of the United States.
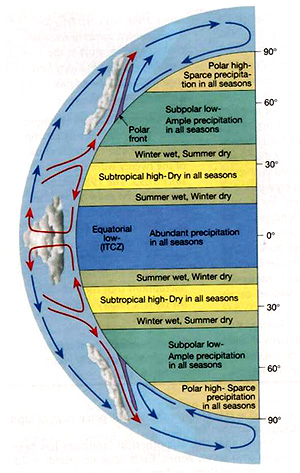
The general features of the global distribution of precipitation can be explained by global winds and pressure systems. In general, regions influenced by high pressure, with its associated subsidence and divergent winds, experience dry conditions. On the other hand, regions under the influence of low pressure and its converging winds and ascending air receive ample precipitation.
On a uniform Earth, throughout most of the year, heavy precipitation would occur in the equatorial region, the midlatitudes would receive most of their precipitation from traveling cyclonic storms, and polar regions would be dominated by cold air that holds little moisture. The most notable anomaly of this zonal distribution of precipitation occurs in the subtropics, where many of the world's great deserts are located. In these regions, pronounced subsidence on the eastern side of subtropical high-pressure centers results in stable atmospheric conditions. Upwelling of cold water along the west coasts of the adjacent continents further adds to the stable and dry conditions. On the other hand, the east coast of the adjacent continent receives abundant precipitation year round due to the convergence and rising air associated with the western side of the oceanic high.
FOR TEST -
TEST 3 NOVEMBER 10TH, Chapter 6, 7 and 8. --
CHAPTER 7 UNDERSTAND -- GOLBAL WIND FLOW- READ PAGES 183- 185 IN BOOK HOW DOES THE WIND FLOW AND WHAT ARE THE NAMES OF THE WIND FLOW - WHAT HAPPENS NEAR
EACH LATITUDE. How does the wind flow at the surface and above the ground. What are the wind scales What is the smallest wind? What is a largest wind scale? WHat are the time frames for the wind scales?